Deep Learning
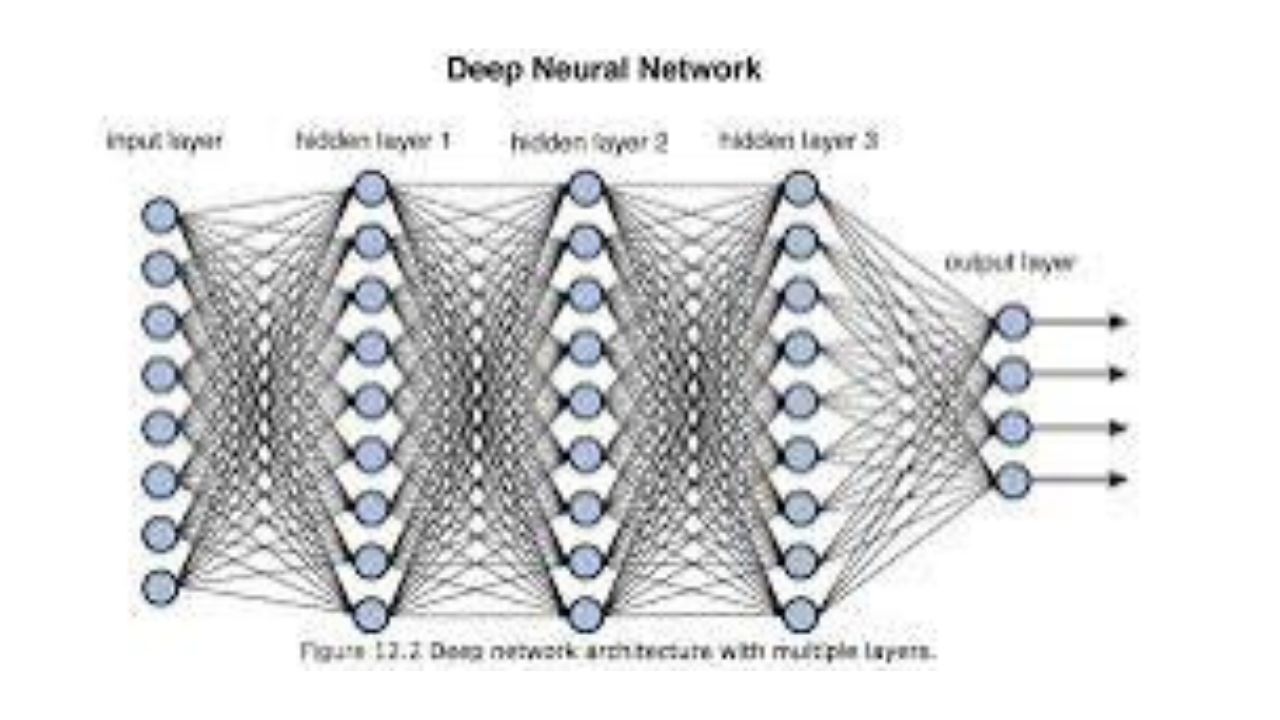
Deep learning is a branch of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks to model and solve complex problems. Deep learning algorithms can automatically learn representations of data at multiple levels of abstraction, making them particularly powerful for tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and speech recognition. Deep learning models typically consist of multiple layers of interconnected artificial neurons organized in a hierarchy of increasing abstraction of the input data. Each layer of neurons learns to identify specific features of the data, and these features are combined in subsequent layers to form higher-level representations. The learning process is typically accomplished using a gradient descent optimization algorithm that adjusts neuron weights to minimize the error between predicted and actual outputs. Some of the most popular deep learning architectures include convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for image and video processing, recurrent neural networks (RNNs) for sequential data processing, and transformers for natural language processing tasks. Deep learning models are characterized by various tasks such as image classification, object recognition, speech recognition, and language translation. The success of deep learning is highly dependent on the availability of large amounts of data and powerful computing resources to enable training of large and complex models. Deep learning has revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence, opening up new possibilities for solving previously unsolvable problems.
Specific Content Keywords : Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,Deep Learning,


