Types of Pumps
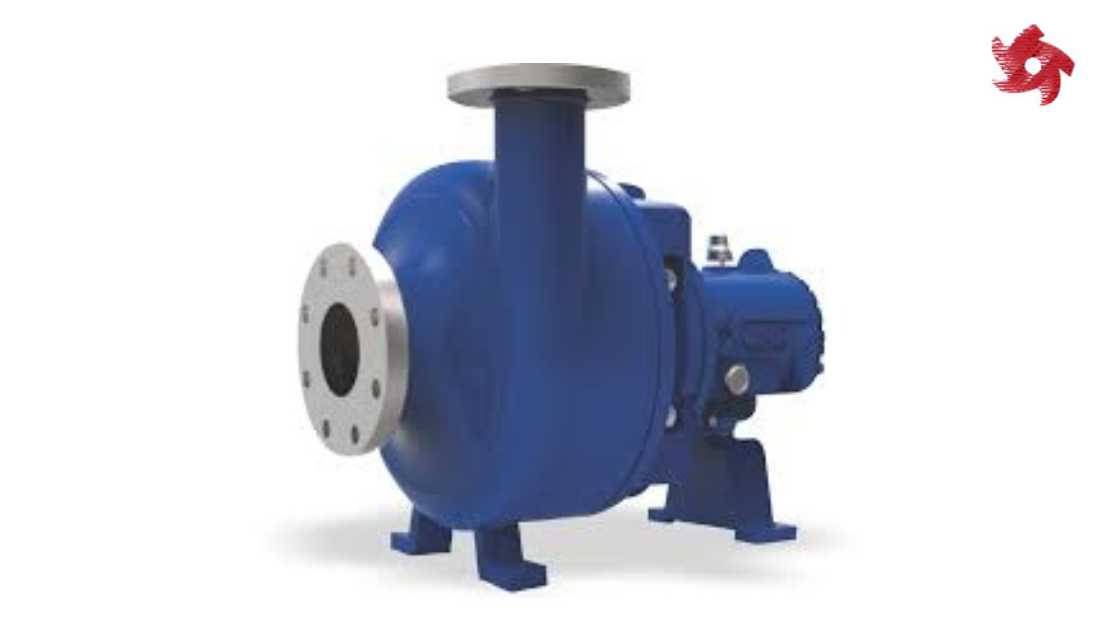
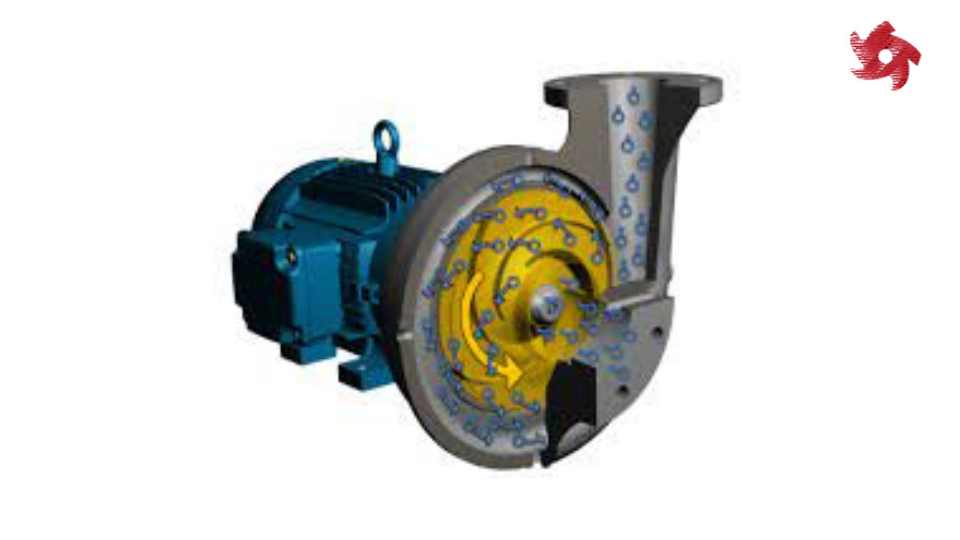
These pumps use centrifugal force to transfer fluids. They are widely used in industries such as water supply, wastewater treatment, chemical processing, and HVAC systems.
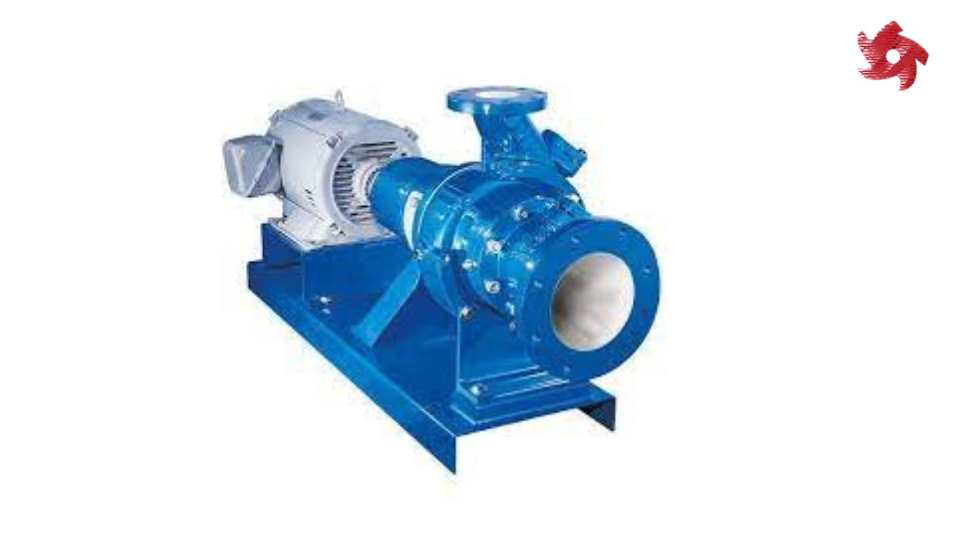
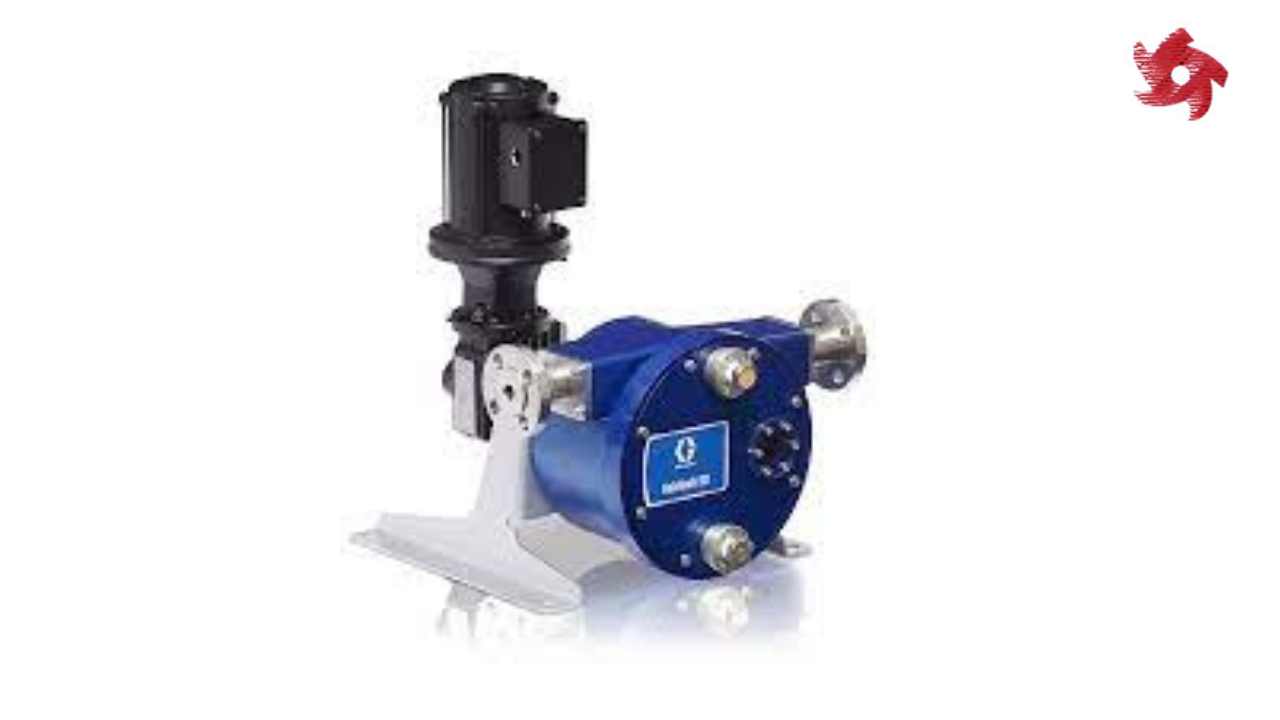
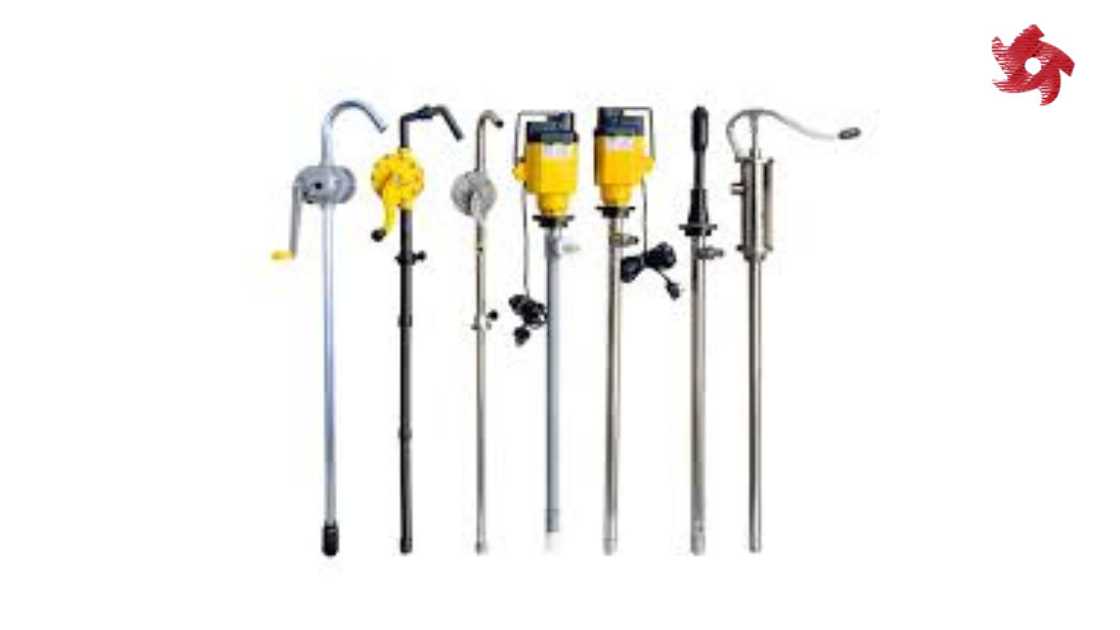
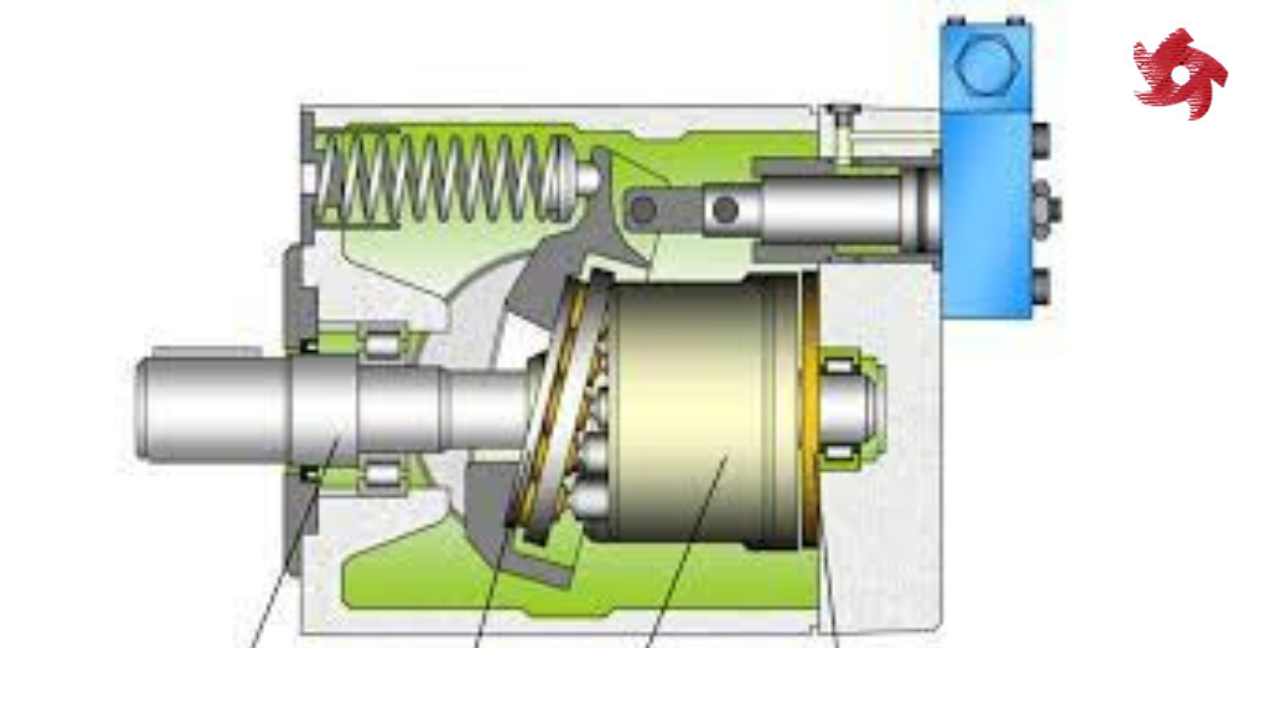
Reciprocating pumps use a piston or plunger to generate pressure and move fluids. They are often used in high-pressure applications and industries like oil and gas, hydraulic systems, and firefighting.
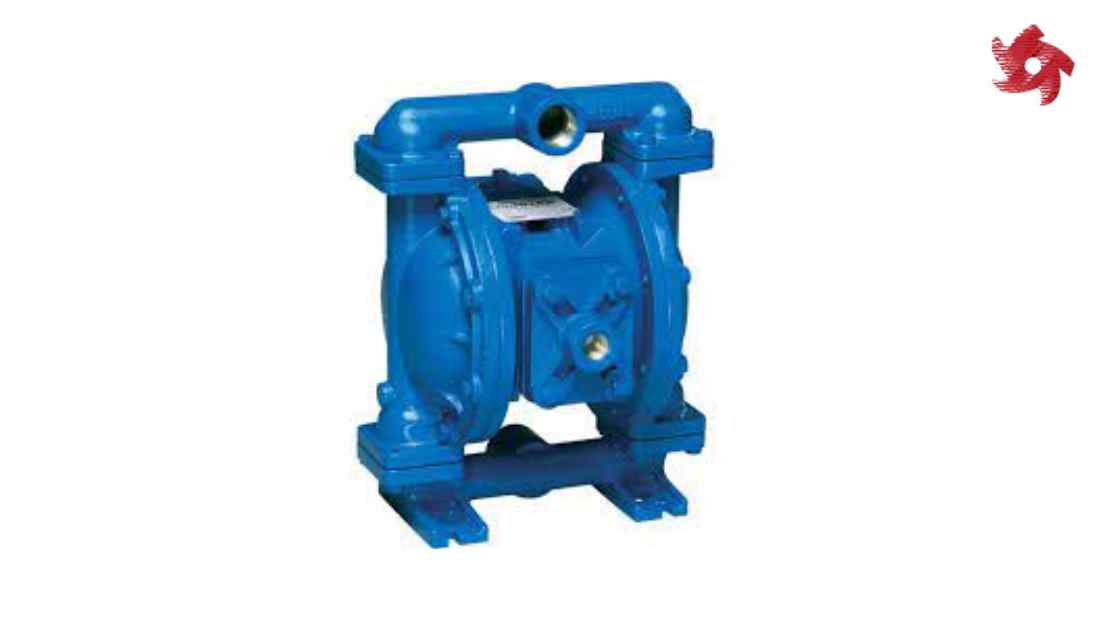
Diaphragm pumps use a flexible diaphragm to displace fluids. They are known for their ability to handle corrosive and viscous fluids, making them suitable for applications in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
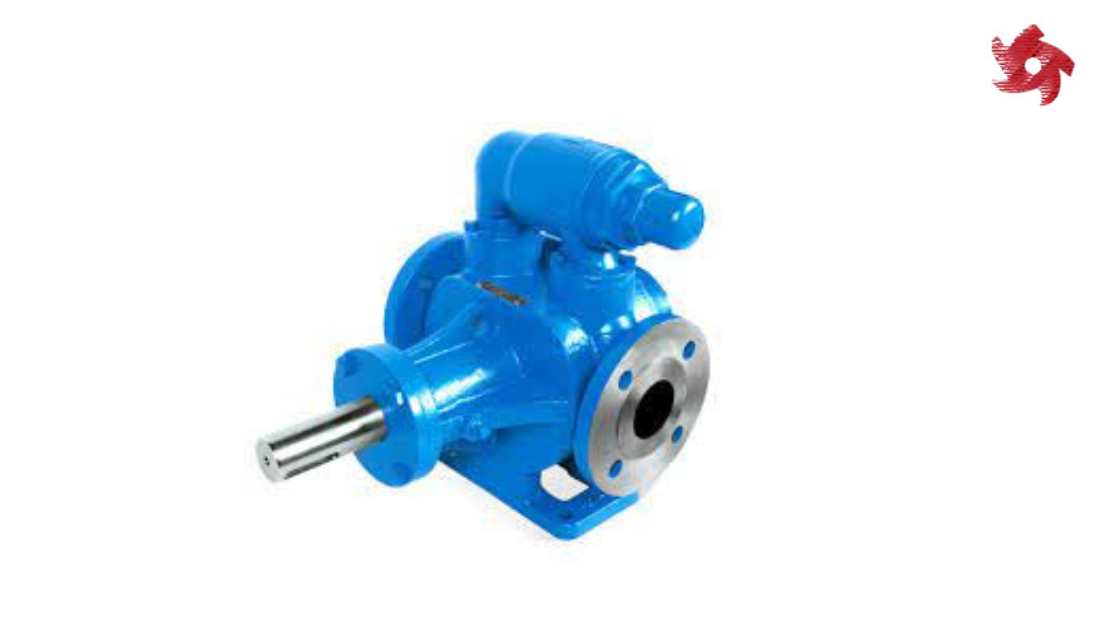
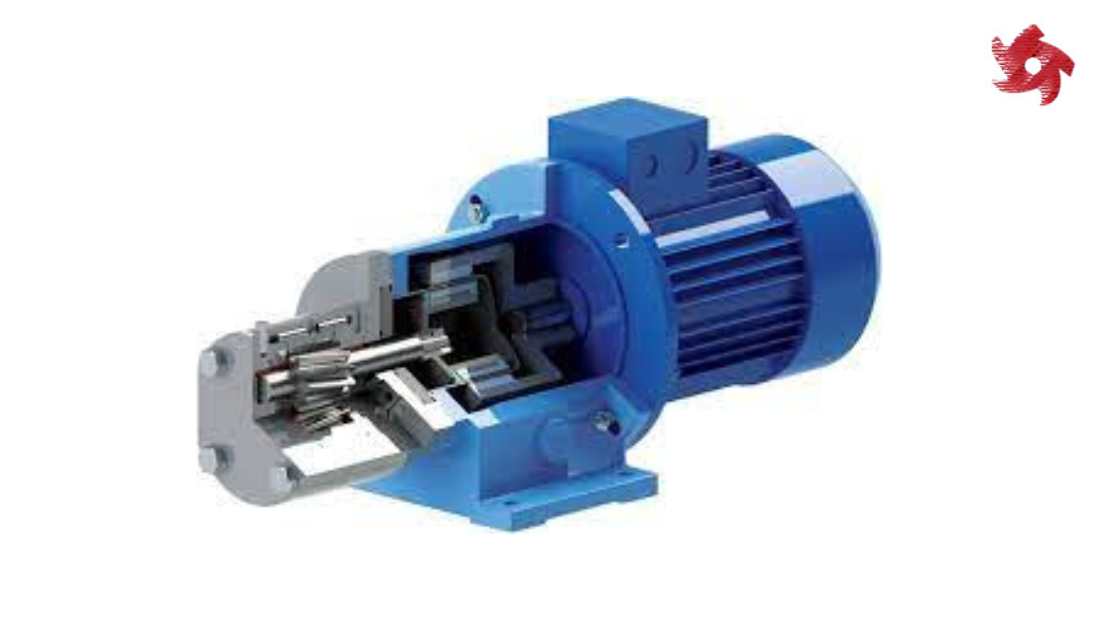
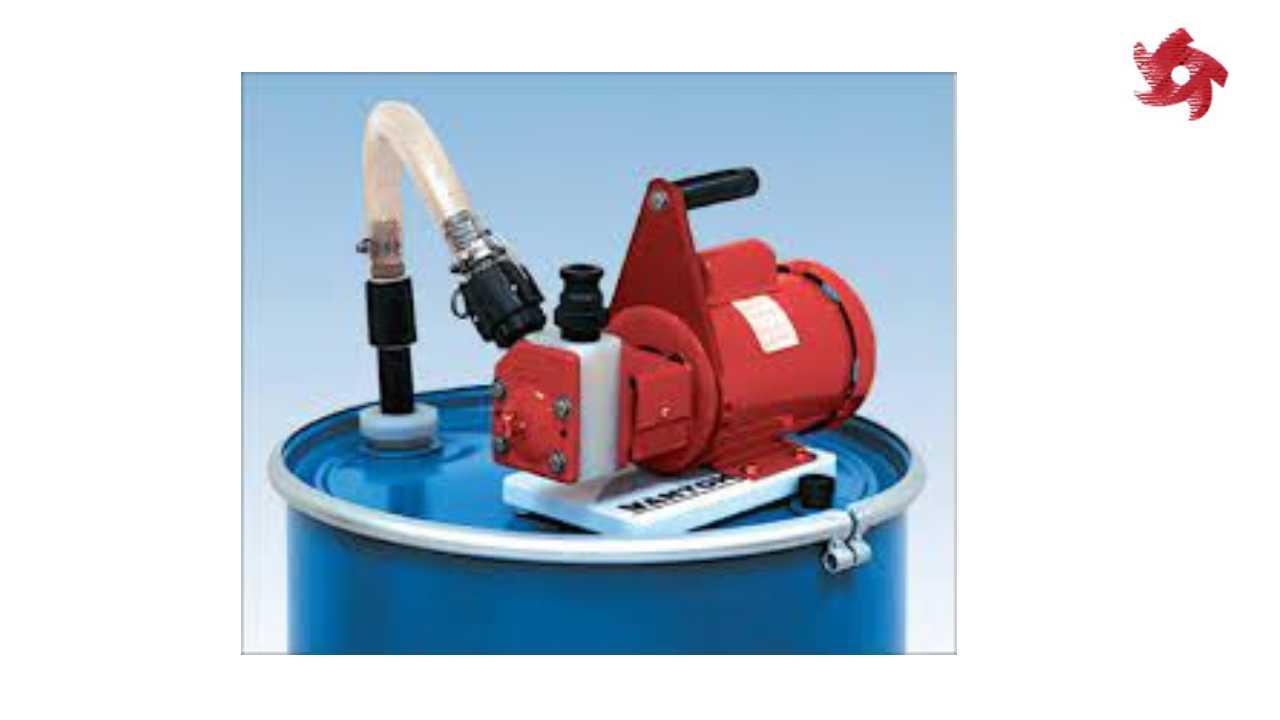
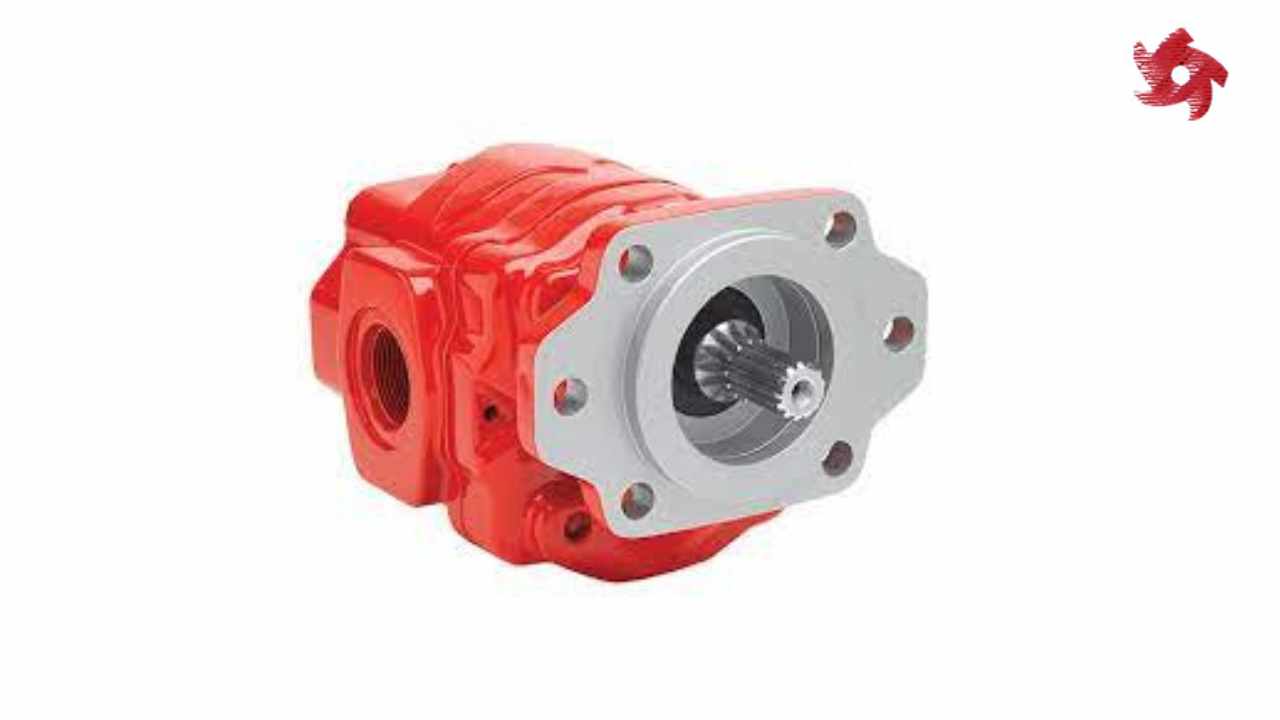
Rotary pumps operate by trapping fluid between rotating components and the pump casing. Examples include gear pumps, vane pumps, and screw pumps. They are commonly used in lubrication systems, fuel transfer, and hydraulic machinery.
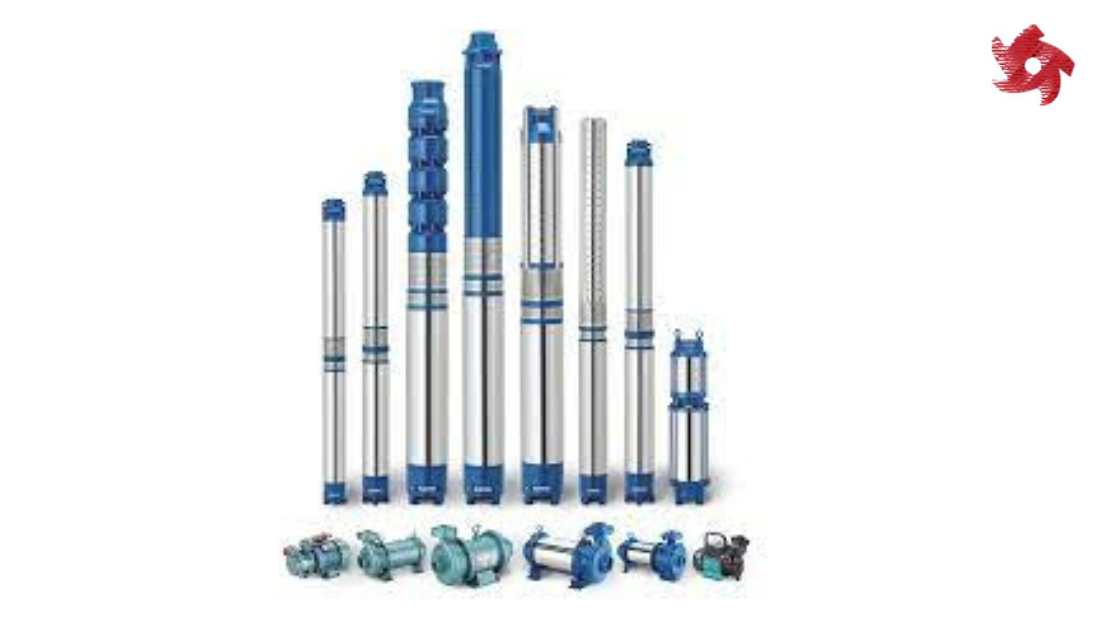
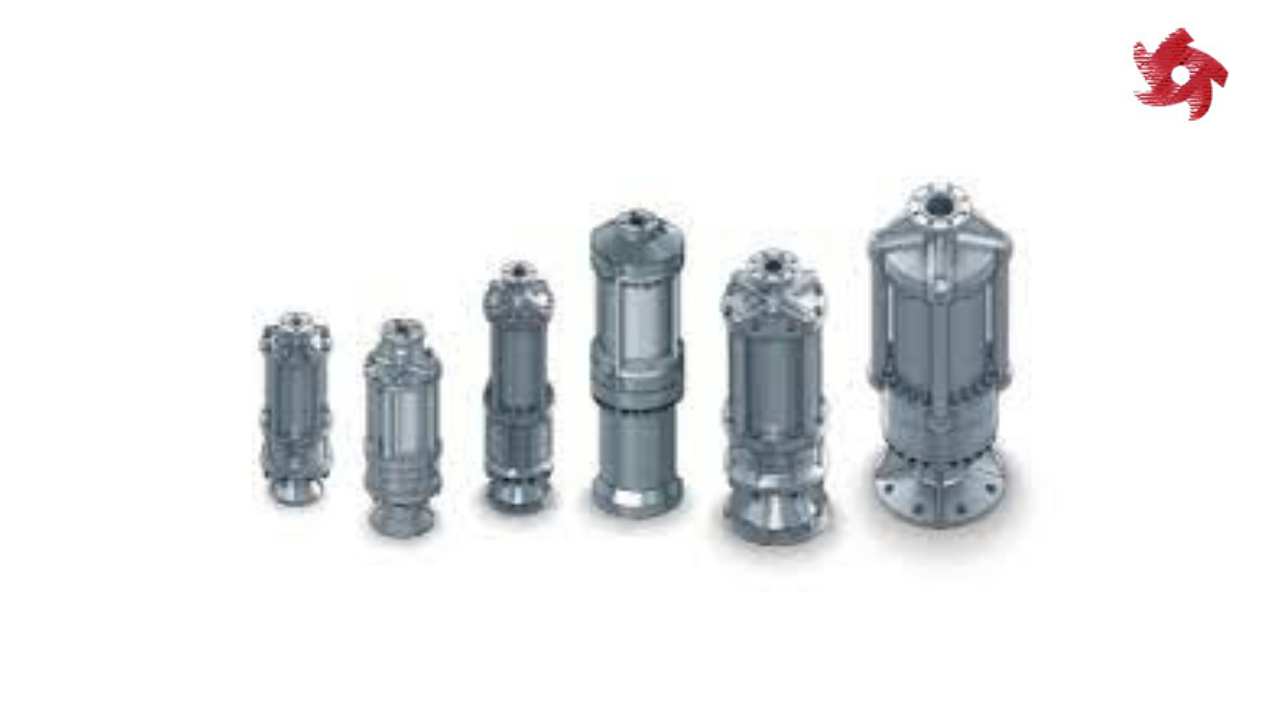
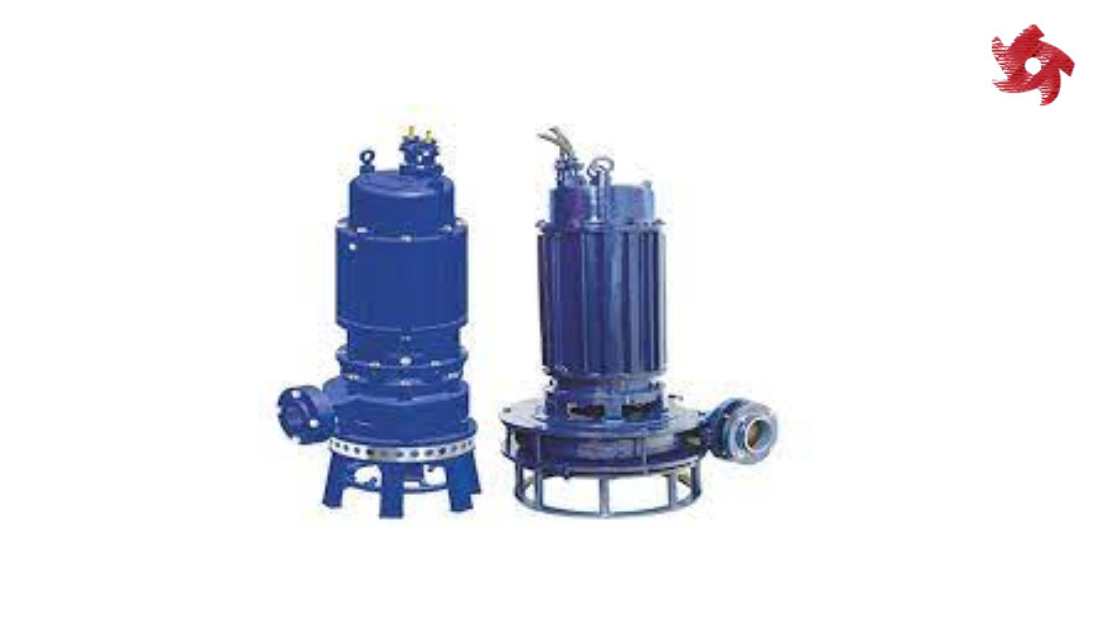
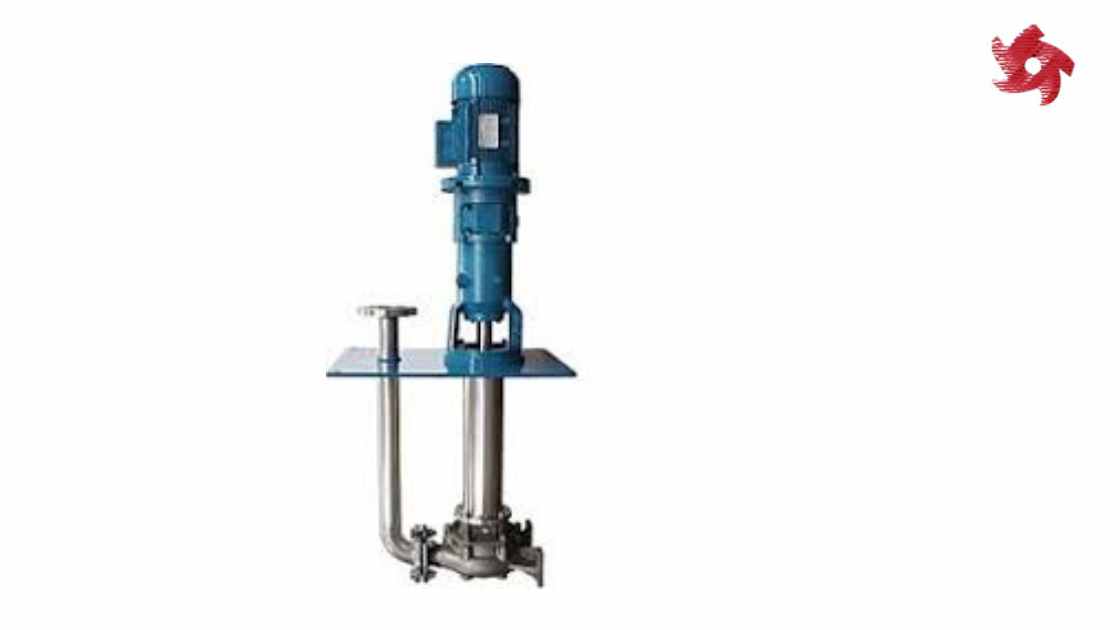
Submersible pumps are designed to be submerged in the fluid they are pumping. They are often used in applications such as groundwater extraction, sewage pumping, and deep well drilling.
Gear pumps use intermeshing gears to pump fluids. They are commonly used in applications requiring precise flow rates, such as metering and dosing systems.
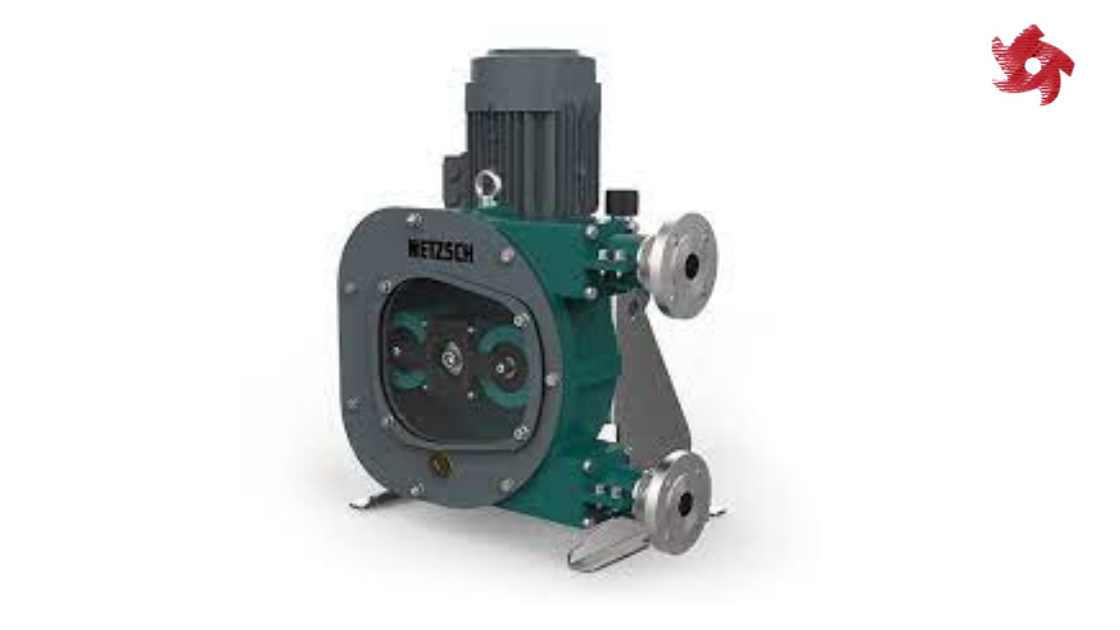
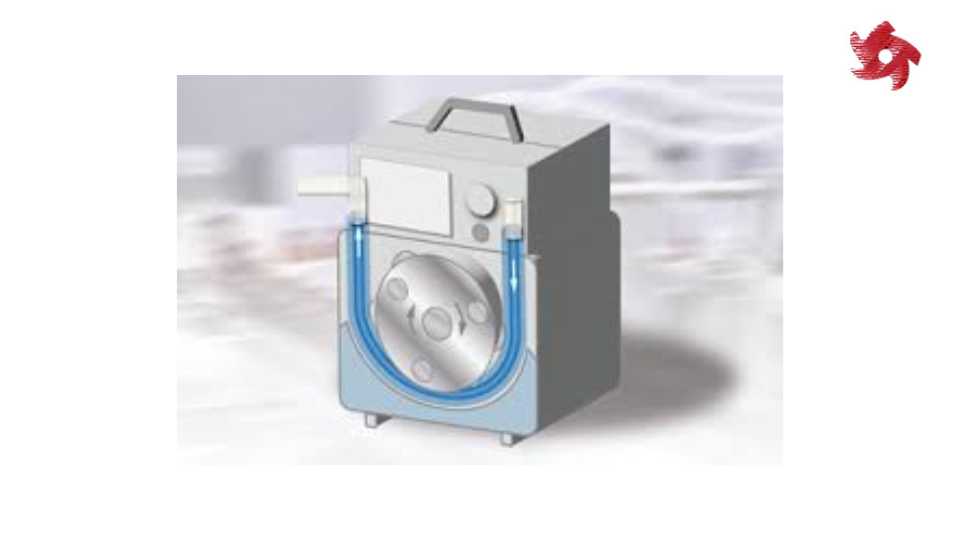
Peristaltic pumps use a squeezing action on a flexible tube to move fluids. They are widely used in the medical field, laboratory applications, and industries where contamination needs to be minimized.
Jet pumps operate by creating a pressure differential using a jet of fluid. They are commonly used for pumping water from wells and in irrigation systems.
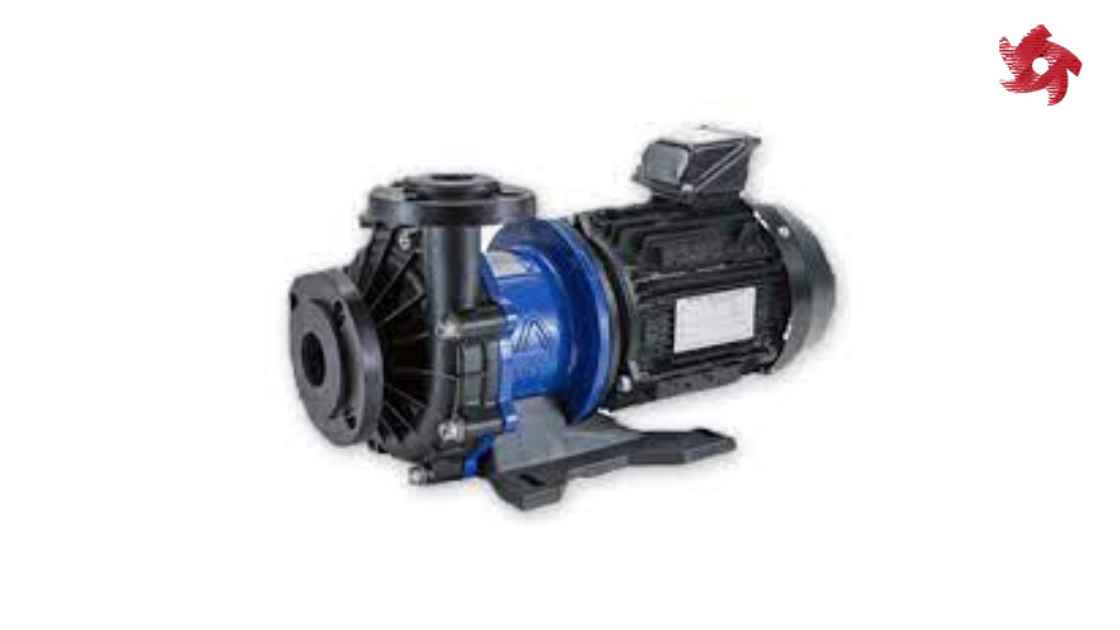
Magnetic drive pumps use a magnetic coupling to transmit power to the impeller without the need for a physical shaft seal. They are often used when leakage or contamination must be avoided, such as in chemical processing and semiconductor manufacturing.
Axial flow pumps move fluid parallel to the pump axis, creating a low-pressure-high-flow environment. They are commonly used in applications like flood control, irrigation, and drainage.
Multistage pumps consist of multiple impellers arranged in series to generate higher pressures. They are commonly used in water supply systems, boiler feed applications, and high-pressure industrial processes.
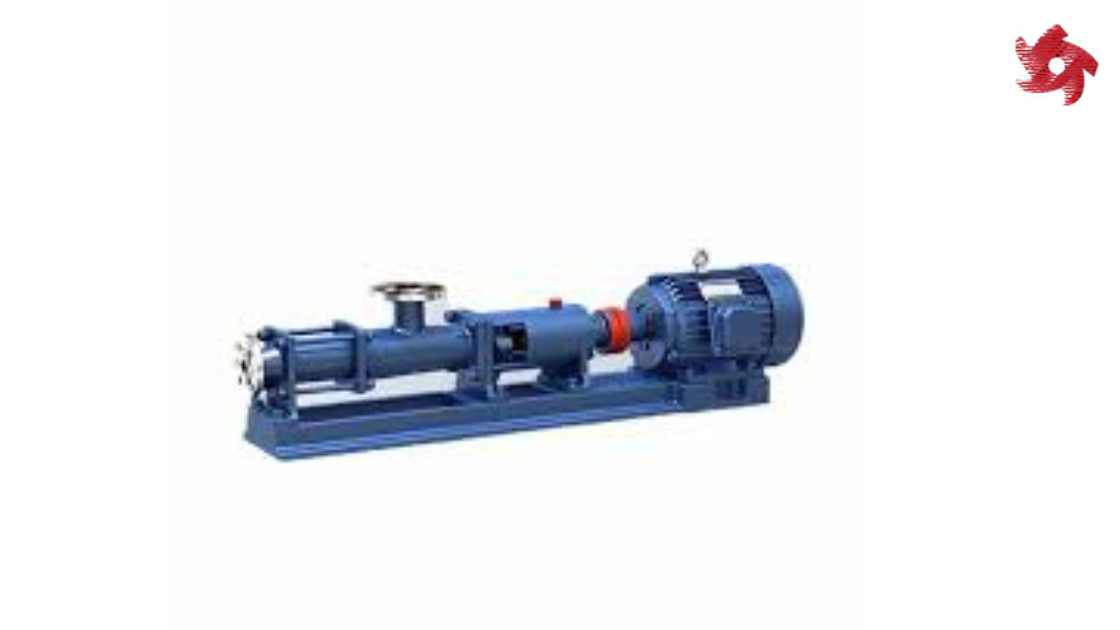
Screw pumps use rotating screws to move fluids along their axis. They are known for their ability to handle viscous fluids and are used in applications such as oil transfer, wastewater treatment, and food processing.
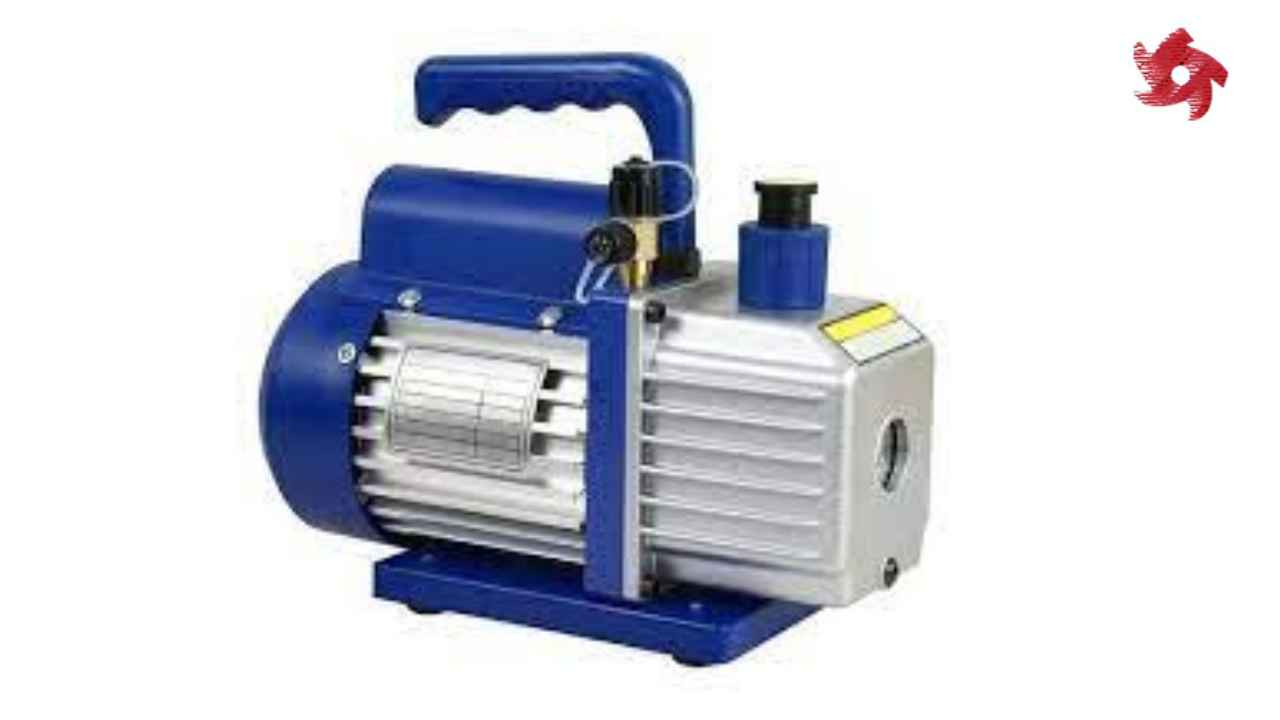
Vacuum pumps are designed to create or maintain a vacuum by removing gas molecules from a sealed chamber. They find applications in industries like pharmaceuticals, electronics manufacturing, and vacuum packaging.
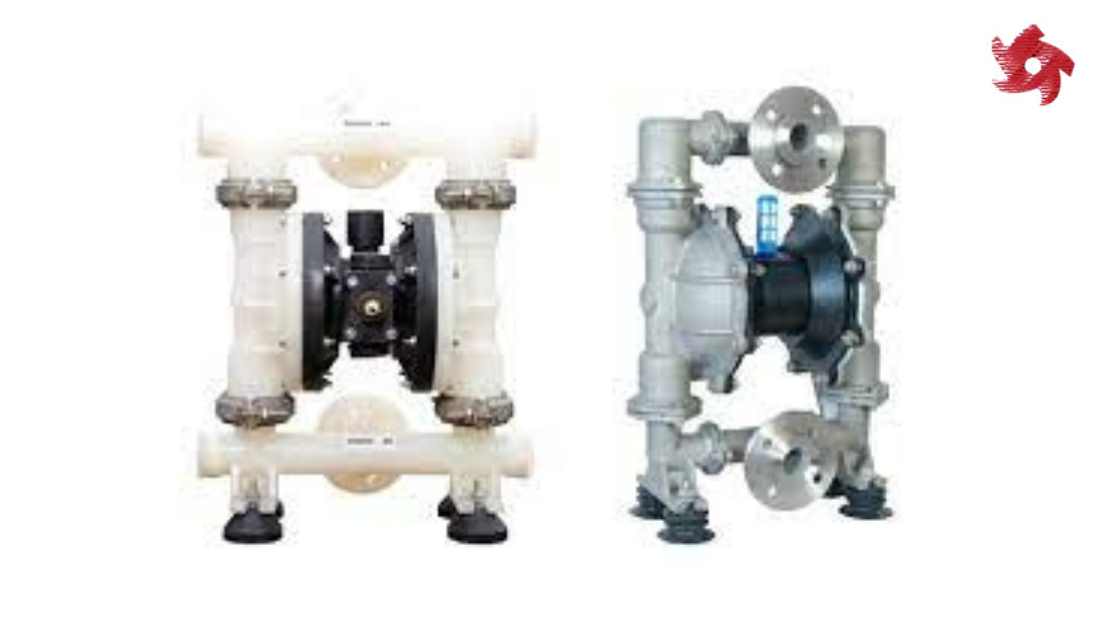
AODD pumps use compressed air to operate diaphragms, creating a pumping action. They are commonly used for handling abrasive, viscous, or shear-sensitive fluids in industries such as mining, chemicals, and food processing.
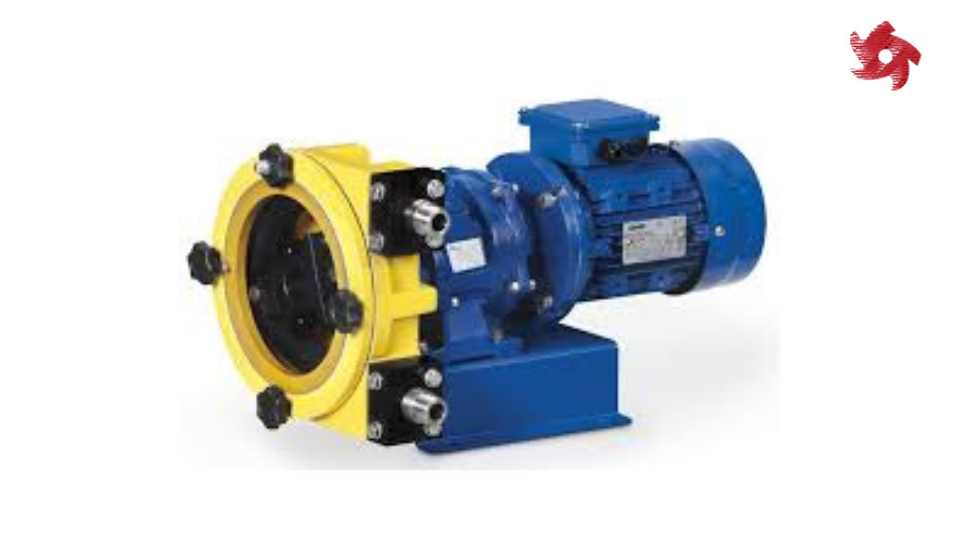
Similar to peristaltic pumps, peristaltic hose pumps use a rotating roller or shoe to compress a flexible hose and move fluids. They are known for their ability to handle abrasive and shear-sensitive fluids and are used in applications such as chemical dosing, mining, and water treatment.
Piston pumps use reciprocating pistons to create pressure and move fluids. They are often used in high-pressure applications, including car wash systems, pressure washers, and hydraulic systems.
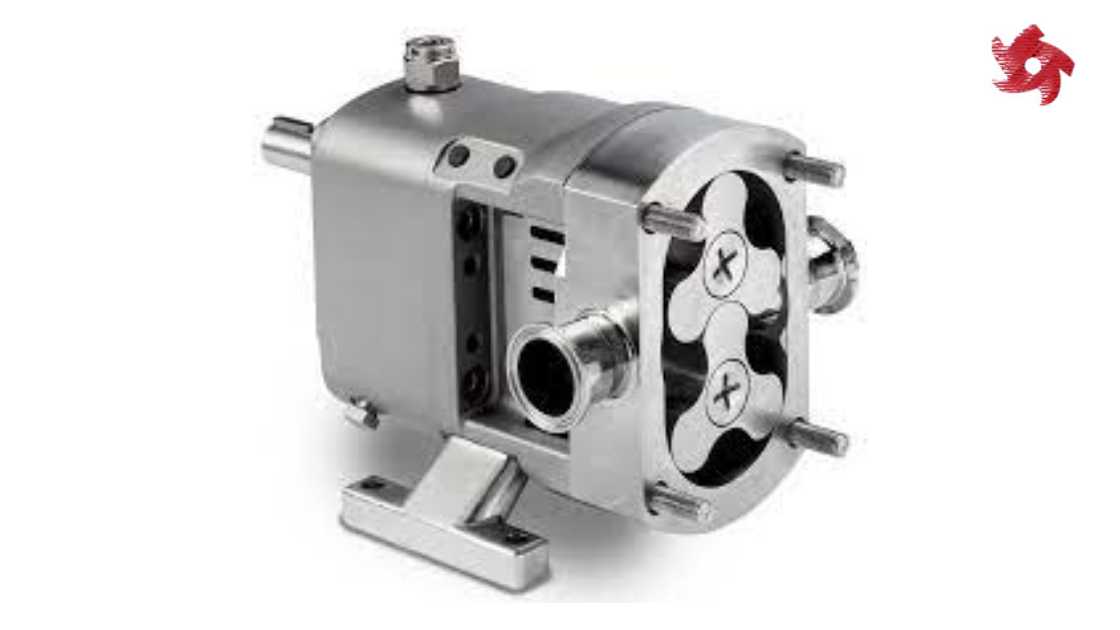
Lobe pumps consist of two or more lobes that rotate in opposite directions, trapping and moving the fluid. They are commonly used in applications involving high-viscosity fluids, such as in the food industry for handling thick sauces and creams.
Peristaltic rotary pumps combine the principles of peristaltic and rotary pumps, using a rotating roller or shoe to compress a flexible tube or hose. They are used for pumping fluids in industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and research laboratories.
Jet or ejector pumps use a high-velocity fluid jet to create a vacuum and draw in and transport fluids. They are commonly used in applications such as pumping liquids with high gas content, mixing and blending fluids, and wastewater treatment.
Regenerative turbine pumps use a rotating impeller with curved blades to create fluid circulation and generate pressure. They are often used in applications requiring high heads and low flow rates, such as refrigeration systems, laser cooling, and fuel cells.
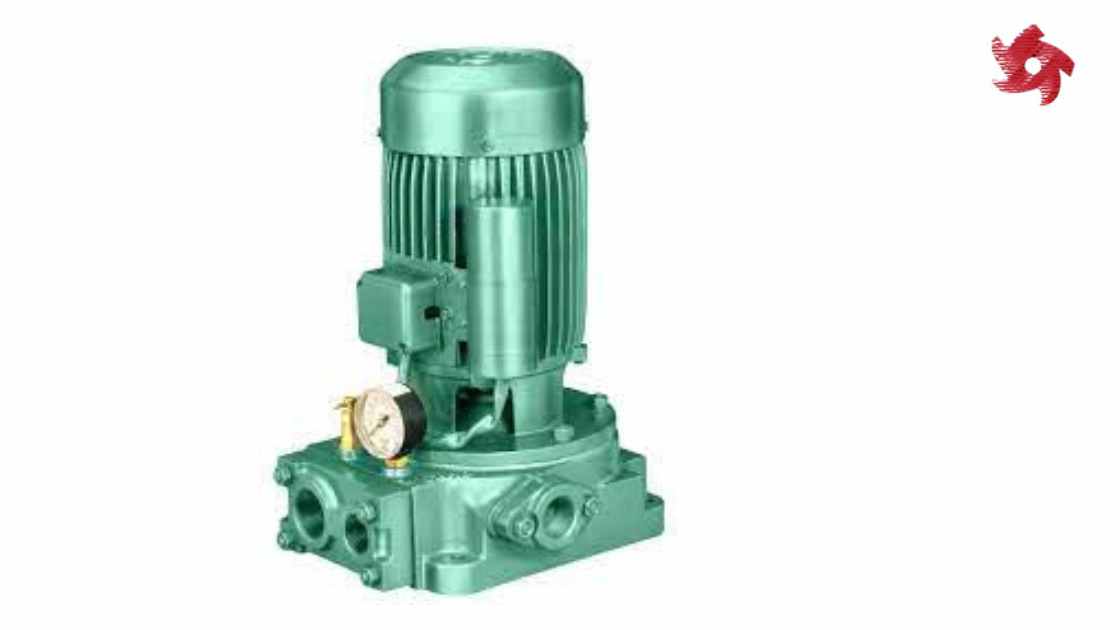
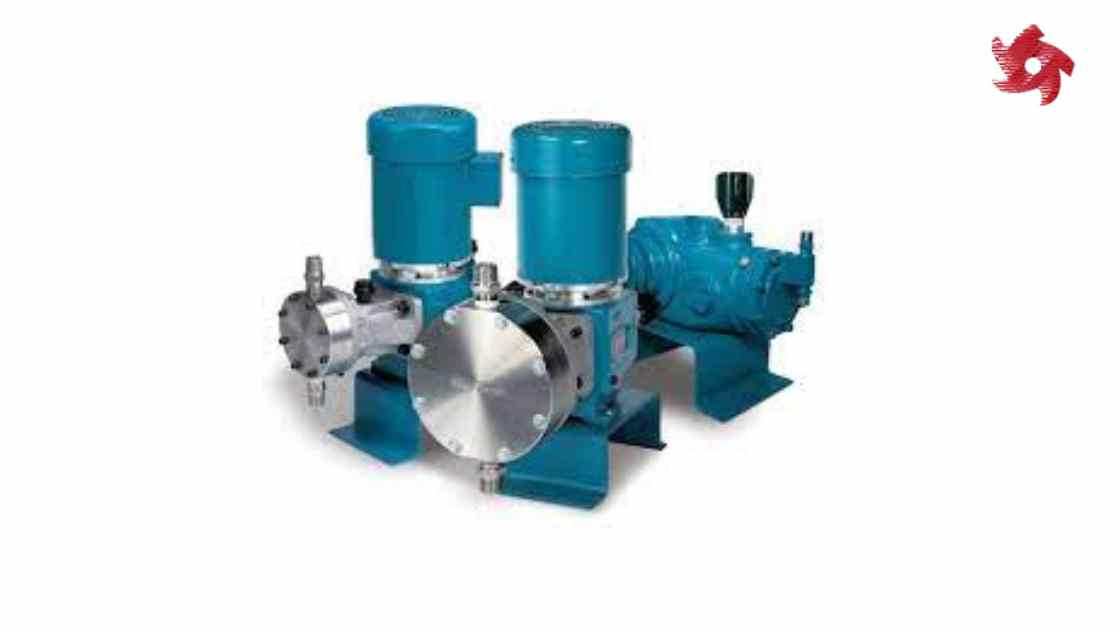
Metering pumps, also known as dosing pumps, are designed to deliver precise and accurate amounts of fluid at predetermined intervals. They are commonly used in applications where precise control of flow rate or chemical dosage is required, such as water treatment, chemical processing, and pharmaceutical production.
Radial flow pumps move fluid perpendicular to the pump axis, creating a high-pressure-low-flow environment. They are often used in applications such as irrigation, sprinkler systems, and water supply for tall buildings.
Peristaltic piston pumps combine the principles of peristaltic and reciprocating pumps. They use a piston-driven mechanism to compress and release a flexible tube, generating a pumping action. These pumps are used in applications that require accurate flow rates and gentle handling of fluids, such as analytical instrumentation and medical devices.
Hydraulic pumps are specifically designed to generate flow and pressure for hydraulic systems. They are commonly used in heavy machinery, construction equipment, and hydraulic power units.
Cryogenic pumps are designed to handle extremely low-temperature fluids, typically below -150 degrees Celsius. They are used in applications such as liquefied natural gas (LNG) processing, cryogenic storage, and superconducting systems.
Peristaltic roller pumps use rotating rollers to compress a flexible tube and move fluids. They are suitable for applications where gentle handling of fluids and precise flow rates are required, such as medical and pharmaceutical applications.
Slurry pumps are specifically designed to handle abrasive and solids-laden fluids, known as slurries. They are commonly used in mining, mineral processing, dredging, and other industries where pumping dense slurry mixtures is necessary.
Peristaltic piston pumps combine the principles of peristaltic and reciprocating pumps. They use a piston-driven mechanism to compress and release a flexible tube, generating a pumping action. These pumps are used in applications that require accurate flow rates and gentle handling of fluids, such as analytical instrumentation and medical devices.
Peristaltic piston pumps combine the principles of peristaltic and reciprocating pumps. They use a piston-driven mechanism to compress and release a flexible tube, generating a pumping action. These pumps are used in applications that require accurate flow rates and gentle handling of fluids, such as analytical instrumentation and medical devices.
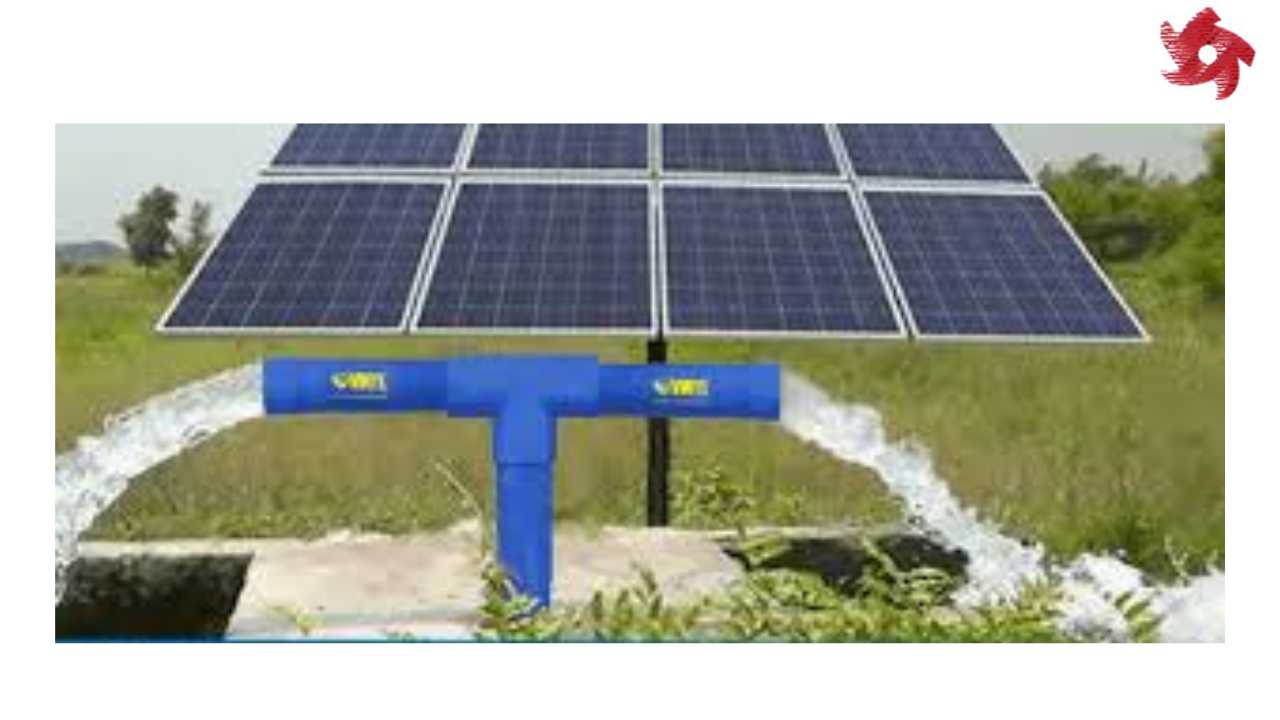
Solar pumps are powered by solar energy and are used in remote areas where electricity supply is limited. They are commonly used for water pumping in irrigation systems, livestock watering, and remote community water supply.